Quick Start
Let's begin with a Microservices example.
Use case
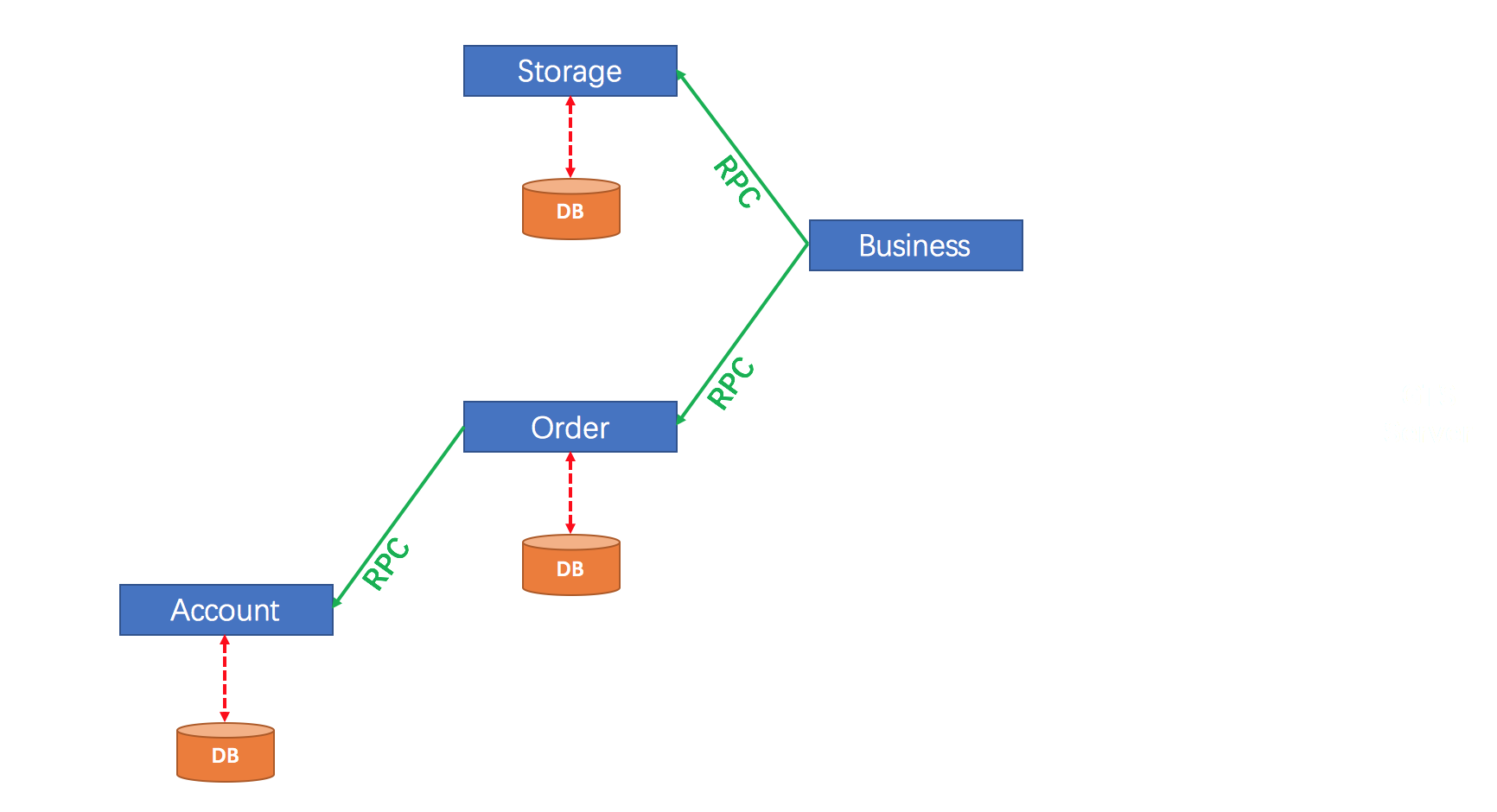
A business logic for user purchasing commodities. The whole business logic is powered by 3 microservices:
- Storage service: deduct storage count on given commodity.
- Order service: create order according to purchase request.
- Account service: debit the balance of user's account.
Architecture
StorageService
public interface StorageService {
/**
* deduct storage count
*/
void deduct(String commodityCode, int count);
}
OrderService
public interface OrderService {
/**
* create order
*/
Order create(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount);
}
AccountService
public interface AccountService {
/**
* debit balance of user's account
*/
void debit(String userId, int money);
}
Main business logic
public class BusinessServiceImpl implements BusinessService {
private StorageService storageService;
private OrderService orderService;
/**
* purchase
*/
public void purchase(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
storageService.deduct(commodityCode, orderCount);
orderService.create(userId, commodityCode, orderCount);
}
}
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
private OrderDAO orderDAO;
private AccountService accountService;
public Order create(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
int orderMoney = calculate(commodityCode, orderCount);
accountService.debit(userId, orderMoney);
Order order = new Order();
order.userId = userId;
order.commodityCode = commodityCode;
order.count = orderCount;
order.money = orderMoney;
// INSERT INTO orders ...
return orderDAO.insert(order);
}
}
Distributed Transaction Solution with SEATA
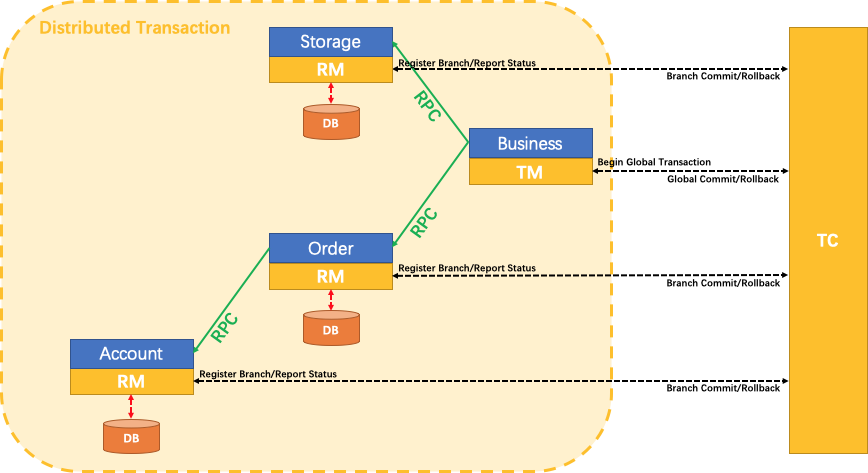
We just need an annotation @GlobalTransactional on business method:
@GlobalTransactional
public void purchase(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
......
}
Example powered by Dubbo + SEATA
Step 1: Setup database
- Requirement: MySQL with InnoDB engine.
Note: In fact, there should be 3 database for the 3 services in the example use case. However, we can just create one database and configure 3 data sources for simple.
Modify Spring XML with the database URL/username/password you just created.
dubbo-account-service.xml dubbo-order-service.xml dubbo-storage-service.xml
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://x.x.x.x:3306/xxx" />
<property name="username" value="xxx" />
<property name="password" value="xxx" />
Step 2: Create UNDO_LOG table
UNDO_LOG table is required by SEATA AT mode. You can obtain the specified version of the undo log SQL script from github.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `undo_log`
(
`branch_id` BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT 'branch transaction id',
`xid` VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL COMMENT 'global transaction id',
`context` VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL COMMENT 'undo_log context,such as serialization',
`rollback_info` LONGBLOB NOT NULL COMMENT 'rollback info',
`log_status` INT(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '0:normal status,1:defense status',
`log_created` DATETIME(6) NOT NULL COMMENT 'create datetime',
`log_modified` DATETIME(6) NOT NULL COMMENT 'modify datetime',
UNIQUE KEY `ux_undo_log` (`xid`, `branch_id`)
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 1 DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4 COMMENT ='AT transaction mode undo table';
ALTER TABLE `undo_log` ADD INDEX `ix_log_created` (`log_created`);
Step 3: Create tables for example business
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `storage_tbl`;
CREATE TABLE `storage_tbl` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`commodity_code` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`count` int(11) DEFAULT 0,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY (`commodity_code`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `order_tbl`;
CREATE TABLE `order_tbl` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`commodity_code` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`count` int(11) DEFAULT 0,
`money` int(11) DEFAULT 0,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `account_tbl`;
CREATE TABLE `account_tbl` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`money` int(11) DEFAULT 0,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
Step 4: Start Server
- Download server package from https://github.com/apache/incubator-seata/releases, unzip it.
Usage: sh seata-server.sh(for linux and mac) or cmd seata-server.bat(for windows) [options]
Options:
--host, -h
The address is expose to registration center and other service can access seata-server via this ip.
Default: 0.0.0.0
--port, -p
The port to listen.
Default: 8091
--storeMode, -m
log store mode : file、db
Default: file
--help
e.g.
sh seata-server.sh -p 8091 -h 127.0.0.1 -m file
Step 5: Run example
Go to samples repo: seata-samples/at-samples, and find a suitable dependency setup. Start Account, Storage, Order, Business services accordingly.